[toc]
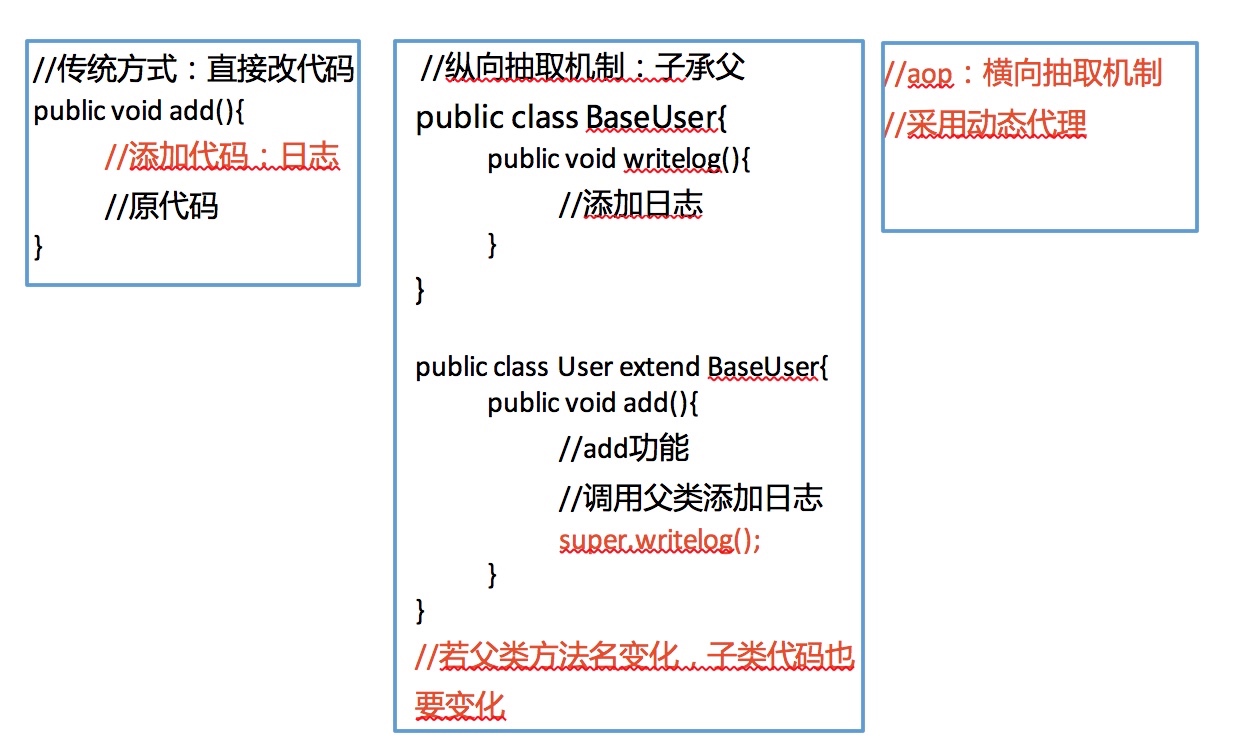
Spring的AOP AOP概述 1. aop:面向切面(方面)编程,扩展功能不修改源代码实现
2. AOP采取**横向抽取**机制,取代了传统纵向继承体系重复性代码
3. aop底层使用动态代理实现AOP底层原理 图解:
动态代理方式–jdk
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class UserDaoProxy public static UserDao getProxy (final UserDao userDao) UserDao proxy = (UserDao)Proxy.newProxyInstance(userDao.getClass().getClassLoader(), userDao.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable System.out.println("AOP增强------" ); if ("add" .equals(method.getName())){ System.out.println("对add方法增强------" ); } return method.invoke(userDao,args); } }); return proxy; } }
动态代理方式–cglib
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class CglibProxy public static BookDaoImpl getProxy () Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer(); enhancer.setSuperclass(BookDaoImpl.class ) ; enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor() { public Object intercept (Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable if ("add" .equals(method.getName())){ System.out.println("add enhance------" ); } return methodProxy.invokeSuper(obj,args); } }); return (BookDaoImpl) enhancer.create(); } }
AOP相关术语 - Joinpoint(连接点): 类里面可以被增强的方法,这些方法称为连接点
- Pointcut(切入点): 所谓切入点是指我们要对哪些Joinpoint进行拦截的定义.
- Advice(通知/增强):所谓通知是指拦截到Joinpoint之后**所要做的事情**就是通知.通知分为前置通知,后置通知,异常通知,最终通知(在后置通知之后执行),环绕通知(切面要完成的功能)
- Aspect(切面): 是切入点和通知(引介)的结合
- Introduction(引介):引介是一种特殊的通知在不修改类代码的前提下, Introduction可以在运行期为类**动态地添加**一些方法或Field.
- Target(目标对象):代理的目标对象(要增强的类)
- Weaving(织入):是把增强应用到目标的过程. 把advice 应用到 target的过程
- Proxy(代理):一个类被AOP织入增强后,就产生一个结果代理类Spring的AOP操作(基于Aspectj的XML方式) 1.在spring里面进行aop操作,使用aspectj实现
(1)aspectj不是spring一部分,和spring一起使用进行aop操作
(2)Spring2.0以后新增了对AspectJ支持
2.使用aspectj实现aop有两种方式
(1)基于aspectj的xml配置
(2)基于aspectj的注解方式jar包
- aopalliance-1.0.jar
- aspectjweaver-1.8.7.jar
- spring-aop-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
- spring-aspects-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar约束
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here --> </beans>
使用表达书配置切入点
- execution(<访问修饰符>?<返回类型><方法名>(<参数>)<异常>)
- 访问修饰符指的是public private 等
- 常用的表达式
1. execution(* cn.itcast.aop.Book.add(..))
2. execution(* cn.itcast.aop.Book.*(..))
3. execution(* *.*(..))
4. 匹配所有save开头的方法 execution(* save*(..))aspectj的aop操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <!--1 配置对象--> <bean id="book" class="com.machine.aop2.Book" /> <bean id="myBook" class="com.machine.aop2.MyBook" /> <!--2 配置AOP操作--> <aop:config> <!--2.1 配置切入点(要增强哪些方法)--> <aop:pointcut id="pointcut1" expression="execution(* com.machine.aop2.Book.*(..))" /> <!--2.2 配置切面(把增强用到方法上)--> <aop:aspect ref="myBook"> <!--配置增强类型--> <!--method: 增强类的使用哪个方法作为增强方法--> <!--前置通知--> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut1" /> <!--后置通知:正常执行--> <aop:after-returning method="after1" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/> <!--出现异常--> <aop:after-throwing method="after3" pointcut-ref="pointcut1" /> <!--最终通知:无论是否方法异常都执行--> <aop:after method="after2" pointcut-ref="pointcut1" /> <!--环绕通知--> <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pointcut1" /> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 //环绕增强 public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable{ System.out.println("环绕前-----"); //执行被增强的方法 proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕后-----"); }
Spring的AOP操作(基于Aspectj的注解方式) 开启 aop 注解的自动代理:
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>AspectJ 的 AOP 的注解:
@Aspect:定义切面类的注解
通知类型:
* @Before
* @AfterReturing
* @Around
* @After
* @AfterThrowing
@Pointcut:定义切入点的注解编写切面类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Aspect public class MyAspectAnno @Before ("MyAspectAnno.pointcut1()" ) public void before () System.out.println("前置通知===========" ); } @Pointcut ("execution(* cn.itcast.spring.demo4.ProductDao.save(..))" ) private void pointcut1 () }
ps: 切面类需要加入Spring的Bean管理
其他通知的注解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 @Aspect public class MyAspectAnno @Before ("MyAspectAnno.pointcut1()" ) public void before () System.out.println("前置通知===========" ); } @AfterReturning ("MyAspectAnno.pointcut2()" ) public void afterReturning () System.out.println("后置通知===========" ); } @Around ("MyAspectAnno.pointcut3()" ) public Object around (ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable System.out.println("环绕前通知==========" ); Object obj = joinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕后通知==========" ); return obj; } @AfterThrowing ("MyAspectAnno.pointcut4()" ) public void afterThrowing () System.out.println("异常抛出通知========" ); } @After ("MyAspectAnno.pointcut4()" ) public void after () System.out.println("最终通知==========" ); } @Pointcut ("execution(* cn.itcast.spring.demo4.ProductDao.save(..))" ) private void pointcut1 () @Pointcut ("execution(* cn.itcast.spring.demo4.ProductDao.update(..))" ) private void pointcut2 () @Pointcut ("execution(* cn.itcast.spring.demo4.ProductDao.delete(..))" ) private void pointcut3 () @Pointcut ("execution(* cn.itcast.spring.demo4.ProductDao.find(..))" ) private void pointcut4 () }
Spring的JDBC的模板 概述 Spring 提供了很多持久层技术的模板类简化编程:
ORM持久化技术
模版类
JDBC
org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplete
Hibernate3
org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.Hibernate3Templete
IBatis(Mybatis)
org.springframework.orm.ibatis.SqlMapClientTemplete
JPA
org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTemplete
开始案例 jar:
spring-jdbc-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar测试类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Test // JDBC模板的基本使用: public void demo1(){ //配置连接池 DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///spring_day03"); dataSource.setUsername("root"); dataSource.setPassword("123"); //JDBC模板 JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource); jdbcTemplate.update("insert into account values (null,?,?)", "小明",10000d); }
将连接池的配置交给 Spring 管理 Spring 内置的连接池的配置 配置连接池
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <!-- 配置 Spring 的内置连接池 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring02"/> <property name="username" value="machine"/> <property name="password" value="4869"/> </bean>
将模板配置到 Spring 中
1 2 3 4 <!-- 配置 JDBC 模板 --> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean>
测试类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class SpringDemo2 { @Resource(name="jdbcTemplate") private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Test public void demo1(){ jdbcTemplate.update("insert into account values (null,?,?)", "小明",10000d); } }
Spring 中配置 DBCP 连接池 jar:
commons-dbcp-1.4.jar
commons-pool-1.5.6.jar配置连接池
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <!-- 配置 DBCP 连接池 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring02"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="123"/> </bean>
配置 c3p0 连接池 jar:
配置连接池
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <!-- 配置 C3P0 连接池 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring02"/> <property name="user" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="123"/> </bean>
ps: 将数据库连接的信息配置到属性文件中
JDBC 模板 CRUD 的操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 public class SpringDemo3 { @Resource(name="jdbcTemplate") private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Test // 插入操作 public void demo1(){ jdbcTemplate.update("insert into account values (null,?,?)", "小明",10000d); } @Test // 修改操作 public void demo2(){ jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=?,money =? where id = ?", " 思雨",10000d,5); } @Test // 删除操作 public void demo3(){ jdbcTemplate.update("delete from account where id = ?", 5); } @Test // 查询一条记录 public void demo4(){ //MyRowMapper 说明了数据表字段和pojo的映射关系 Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from account id = ?", new MyRowMapper(), 1); System.out.println(account); } @Test // 查询所有记录 public void demo5(){ List<Account> list = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account", MyRowMapper()); for (Account account : list) { System.out.println(account); } } /* MyRowMapper 继承 RowMapper<pojo类> 接口, mapRow方法手动说明了 表字段和pojo的映射关系 */ class MyRowMapper implements RowMapper<Account>{ @Override public Account mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException { Account account = new Account(); account.setId(rs.getInt("id")); account.setName(rs.getString("name")); account.setMoney(rs.getDouble("money")); return account; } } }
Spring的事务 事务概述 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 - 什么是事务: 事务逻辑上的一组操作,组成这组操作的各个逻辑单元,要么一起成功,要么一起失败. - 事务特性: 原子性 :强调事务的不可分割. 一致性 :事务的执行的前后数据的完整性保持一致. 隔离性 :一个事务执行的过程中,不应该受到其他事务的干扰 持久性 :事务一旦结束,数据就持久到数据库 - 如果不考虑隔离性引发安全性问题: 脏读 :一个事务读到了另一个事务的未提交(commit)的数据 不可重复读 :一个事务读到了另一个事务已经提交的 update 的数据,导致多次查询结果不一致. 虚读 :一个事务读到了另一个事务已经提交的 insert 的数据导致多次查询结果不一致. - 解决读问题:设置事务隔离级别 未提交读 :脏读,不可重复读,虚读都有可能发生 已提交读 :避免脏读。但是不可重复读和虚读有可能发生 可重复读 :避免脏读和不可重复读.但是虚读有可能发生. 串行化的 :避免以上所有读问题.
Spring进行事务管理 相关的类和API 1. PlatformTransactionManager接口 -- 平台事务管理器.(真正管理事务的类)。该接口有具体的实现类,根据不同的持久层框架,需要选择不同的实现类!
2. TransactionDefinition接口 -- 事务定义信息.(事务的隔离级别,传播行为,超时,只读)
3. TransactionStatus接口 -- 事务的状态
4. 总结:上述对象之间的关系:
平台事务管理器 真正管理事务对象.
根据事务定义的信息TransactionDefinition 进行事务管理,
在管理事务中产生一些状态.将状态记录到TransactionStatus中
5. PlatformTransactionManager接口中实现类和常用的方法
1. 接口的实现类(真正管理事务的对象)
* 使用 Spring JDBC 或 iBatis 进行持久化数据时使用
org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
* 使用 Hibernate 版本进行持久化数据时使用
org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager
2. 该接口的常用方法
* void commit(TransactionStatus status)
* TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition)
* void rollback(TransactionStatus status)
6. TransactionDefinition(采用默认)
1. 事务隔离级别的常量
* static int ISOLATION_DEFAULT -- 采用数据库的默认隔离级别
* static int ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED -- 未提交
* static int ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED -- 已提交
* static int ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ -- 可重复
* static int ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE -- 串行化
2. 事务的传播行为常量(不用设置,使用默认值)
* 先解释什么是事务的传播行为:解决的是业务层之间的方法调用!!例如:A调用B
* 保证A,B在同一个事务中
* PROPAGATION_REQUIRED(默认值) -- 若A中有事务,B使用A中的事务(不用再开 ).如果没有,B就会开启一个新的事务,并将A包含进来.默认值!!
* PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS -- A中有事务,使用A中的事务.如果A中没有事务.那么B也不使用事务.
* PROPAGATION_MANDATORY -- A中有事务,使用A中的事务.如果A没有事务.抛出异常.
* 保证A,B没有在一个事务中
* PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW(记)-- A中有事务,将A中的事务挂起.B创建一个新的事务.
* PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED -- A中有事务,将A中的事务挂起.
* PROPAGATION_NEVER -- A中有事务,抛出异常.
* PROPAGATION_NESTED(记) -- 嵌套事务.当A执行之后,就会在这个位置设置一个保存点.如果B没有问题.执行通过.如果B出现异常,运行客户根据需求回滚(选择回滚到保存点或者是最初始状态) Spring 的编程式事务管理(不用) 手动编写代码完成事务的管理:
配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- 配置事务管理模板 --> <bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/> </bean>
需要在业务层注入事务管理模板
1 2 3 4 5 6 <!-- 配置业务层的类 --> <bean id="accountService" class="cn.itcast.transaction.demo1.AccountServiceImpl"> <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/> <!-- 注入事务管理模板 --> <property name="transactionTemplate" ref="transactionTemplate"/> </bean>
手动编写代码实现事务管理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public void transfer(final String from, final String to, final Double money) { //Spring注入 transactionTemplate transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() { @Override protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus status){ accountDao.outMoney(from, money); int d = 1 / 0; accountDao.inMoney(to, money); } }); }
Spring的声明式事务管理: XML方式 - 思想就是AOP
- 不需要进行手动编写代码,通过一段配置完成事务管理配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 <!-- 事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- 配置事务增强(advice:通知):对哪些方法事务增强 --> <!--* 注意:如果是自己编写的切面,使用<aop:aspect>标签,如果是系统制作的,使用<aop:advisor>标签。--> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <!-- tx:method的一些属性 name :绑定事务的方法名,可以使用通配符,可以配置多个。 //以下采用默认值即可 propagation="REQUIRED" :传播行为-保证A,B在同一个事务中 isolation="DEFAULT" :隔离级别-数据库默认级别 read-only="false" :是否只读-否 timeout="-1" :过期时间 rollback-for="" :发生哪些异常回滚. no-rollback-for="" :发生哪些异常不回滚. --> <!-- 对哪些方法加事务 --> <tx:method name="save*" /> <tx:method name="update*" /> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 配置AOP切面产生代理 --> <aop:config> <!--配置事务通知,切入点--> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* execution(* com.machine.tx.Book.*(..))"/> </aop:config>
测试类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Demo2 { @Resource(name="accountService") private AccountService accountService; @Test public void run1(){ accountService.pay("小白", "大白", 1000); } }
Spring的声明式事务管理: 注解方式(推荐) 配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- 开启注解事务 --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
在业务层上添加一个注解 : @Transactional
Spring整合WEB项目 整合原理 1. 老方法加载Spring核心配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
//可行,但效率低
2. 实现思想:把加载文件和创建对象,放在服务器启动时完成。
3. 实现原理:
* ServletContext对象,ServletContext监听器
* 具体过程:
* 服务器启动,一个项目会创建一个ServletContext;
* 监听器监听到ServletContext创建,就加载配置文件,创建配置文件里的对象;
* 用setAttribute方法将对象放入ServletContext域,用getAtrribute方法从ServletContext域中取出对象整合实例 jar包:添加
- spring-web-4.2.4.RELEASE.jarweb.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns ="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id ="WebApp_ID" version ="2.5" > <display-name > spring_day01</display-name > <context-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:bean.xml</param-value > </context-param > <listener > <listener-class > org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class > </listener > <welcome-file-list > <welcome-file > index.html</welcome-file > <welcome-file > index.htm</welcome-file > <welcome-file > index.jsp</welcome-file > <welcome-file > default.html</welcome-file > <welcome-file > default.htm</welcome-file > <welcome-file > default.jsp</welcome-file > </welcome-file-list > </web-app >