笔记参考:
慕课网【2小时学会SpringBoot】
《JavaEE开发的颠覆者 Spring Boot实战 》
[TOC]
1 Spring Boot开始
1.1 SpringBoot介绍
- SpringBoot和SpringMVC的关系:SpringBoot是SpringMVC的升级版,两者没有必然的联系
- SpringBoot的特点
1.化繁为简,简化配置
2.备受关注,是下一代框架
3.微服务的入门级微框架
- 微服务
SpringBoot -> SpringCloud -> 微服务
- 课程目录
1.第一个SpringBoot程序
- 官方文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.0.0.RELEASE/reference/html/ 1.2 第一个SpringBoot应用
使用IntelliJ IDEA
具体步骤:
new prpject
-> spring initializr
->Defaut
-> web-->web应用创建成功后,会生成相应的目录和文件。
其中有一个Application类,它是程序的入口:表示启动springboot
@SpringBootApplication
public class FirstspringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FirstspringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}springboot就是一个maven工程
写一个HelloController:
@RestController //等同于同时加上了@Controller和@ResponseBody
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String say(){
return "hello spring boot";
}
}运行 Application的main(),会启动,由于springboot自动内置了servlet容器,所以不需要类似传统的方式,先部署到容器再启动容器。
http://localhost:8080/hello, 就可以在浏览器上看到
Application启动类类放在最外侧,即包含所有子包
原因:spring-boot会自动加载启动类所在包下及其子包下的所有组件.
其他启动项目的方式:
2. 进入项目根目录,在命令行写:
mvn spring-boot:run
3. 进入项目>target目录,有jar文件
java -jar myspringboot-0.0.1-SNAPAHOT.jar1.3 项目属性配置
两种配置文件
默认application.properties文件
server.port=8081
server.context-path=/sb推荐application.yml
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: /sb
port:[空格]8081 ,yml语法必须有空格
访问:http://localhost:8081/sb/hello
自定义的属性
yml:
server:
port: 8080
context-path: /sb
girl:
name: B
age: 18
content: "name: ${name},age: ${age}"pojo:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "girl") //将yml文件中前缀为girl 的属性 注入到 此类
@Component //bean交给Spring管理
public class Girl {
private String name;
private String age;
private String content;
//set get
}controller:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
//注入配置文件里的name值
@Value("${girl.name}")
private String name;
//自动注入
@Autowired
private Girl girl;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String say(){
String s = name+"===="+girl;
return s;
}
}多环境配置
application.yml
spring:
profiles:
active: dev用于开发环境的application-dev.yml
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: /sb
girl:
name: 大白
age: 18
content: "name: ${girl.name},age: ${girl.age}"1.4 Controller的简单使用
@Controller
@RestController: Spring4引入,@Controller+ @ResponseBody
@RequestMapping获取参数
@PathVariable: 获取url中的数据
@RequestParam:获取请求参数的值
@GetMapping: 组合注解@PathVariable
@RequestMapping("/hello/{id}")
public String say(@PathVariable Integer id){
return id.toString();
}@RequestParam
若url格式为 http://localhost:8081/sb/hello?id=100
则使用@RequestParam
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String say(@RequestParam("id") Integer id){
return id.toString();
}@GetMapping,@PostMapping
是组合注解,@GetMapping=@RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.GET)2 SpringBoot运行原理
2.1 自动配置
自动配置原理:基于条件配置bean
关于自动配置的源码包:
查看启用和未启用的自动配置:
在yml文件中添加。debug: true
启动后控制台会输出Positive matches:(已启用)和Negative matches:(未启用)
2.2 运作原理
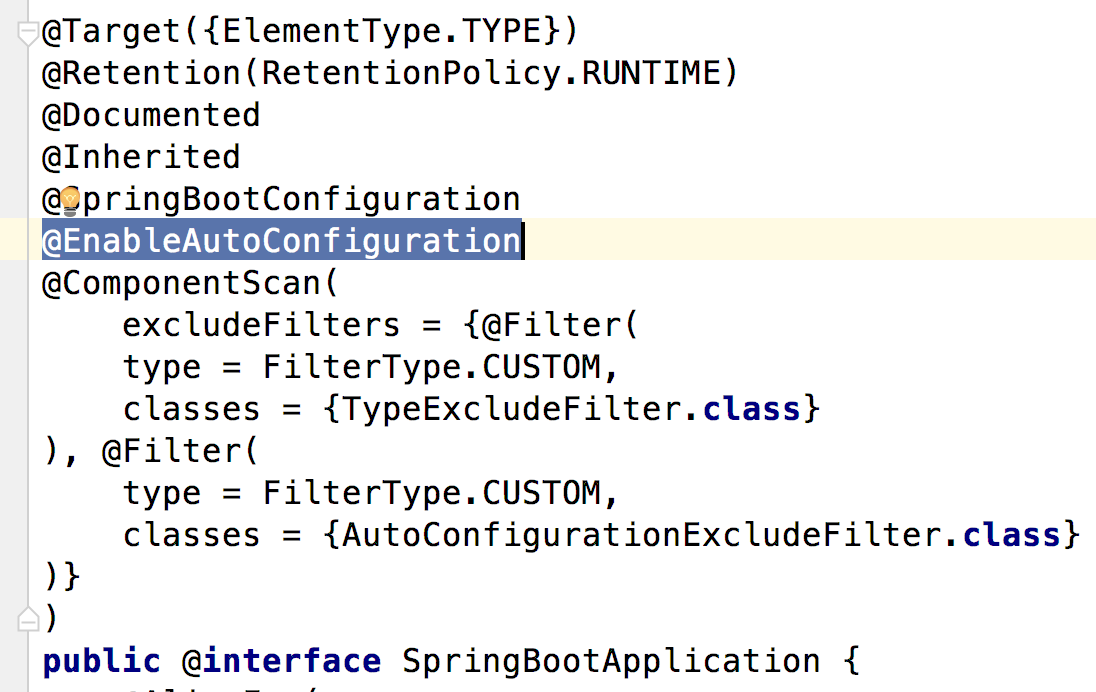
@SpringBootApplication注解是一个组合注解,源码如下
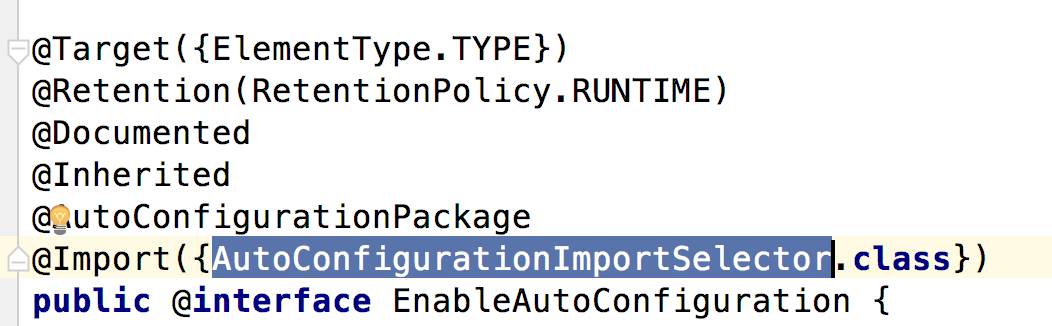
它的核心功能由@EnableAutoConfiguration提供。@EnableAutoConfiguration源码如下:
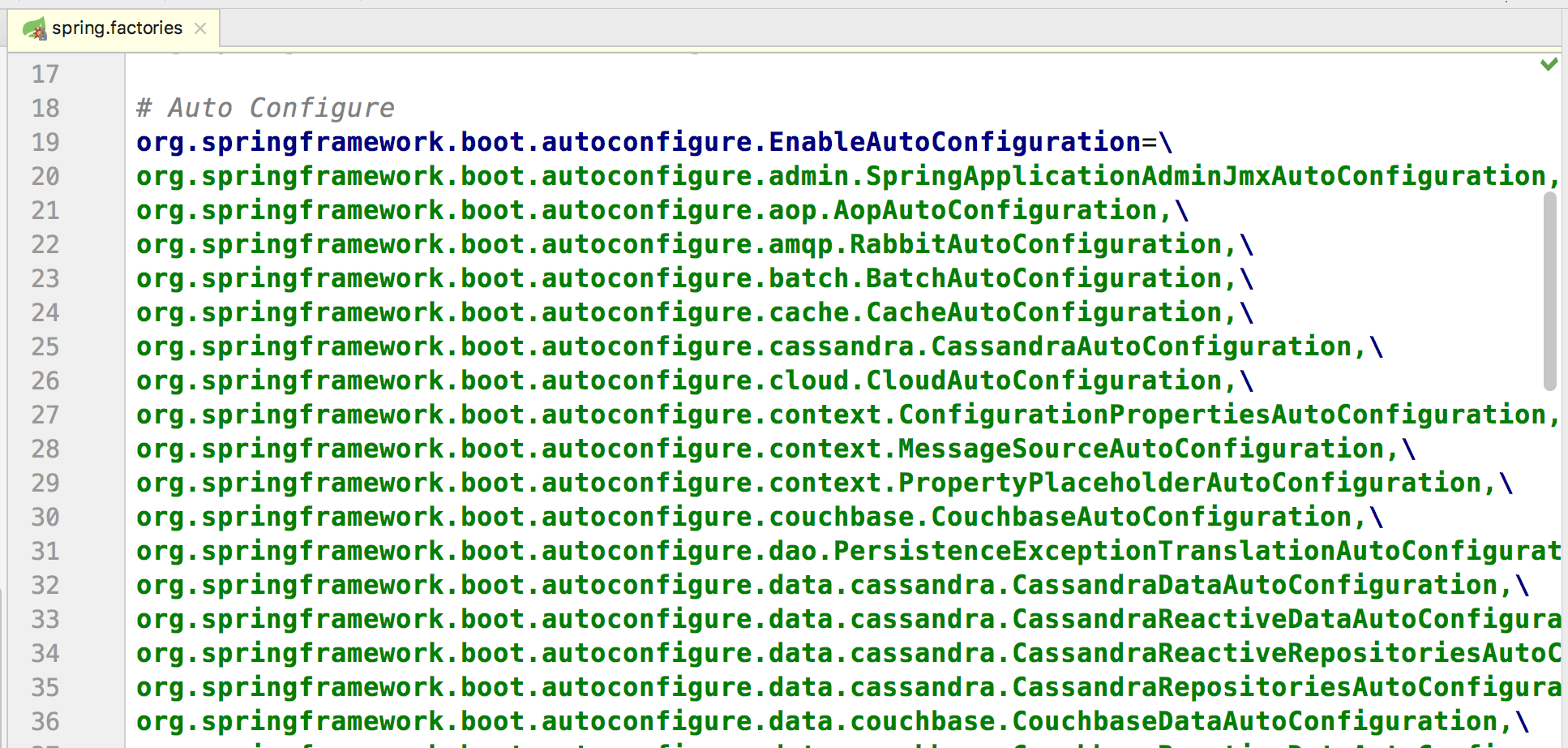
AutoConfigurationImportSelector使用SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames方法扫描具有META-INF/spring.factories文件的jar包。
打开spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.0.2.RELEASE.jar的spring.factories,查看文件中声明了哪些自动配置
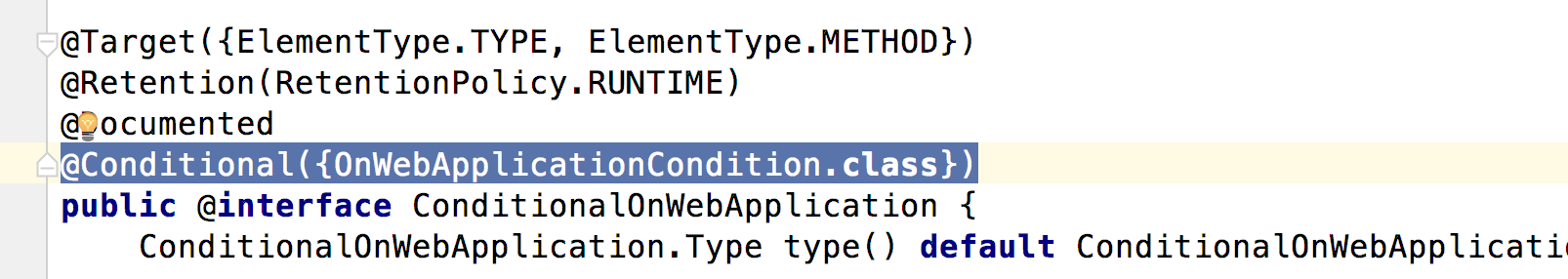
2.3 核心注解
简单分析@ConditionalOnWebApplication注解
能看出,此注解使用的条件是:OnWebApplicationCondition,下面看这个条件是如何构造的,
从isWebApplication方法可以看出判断条件
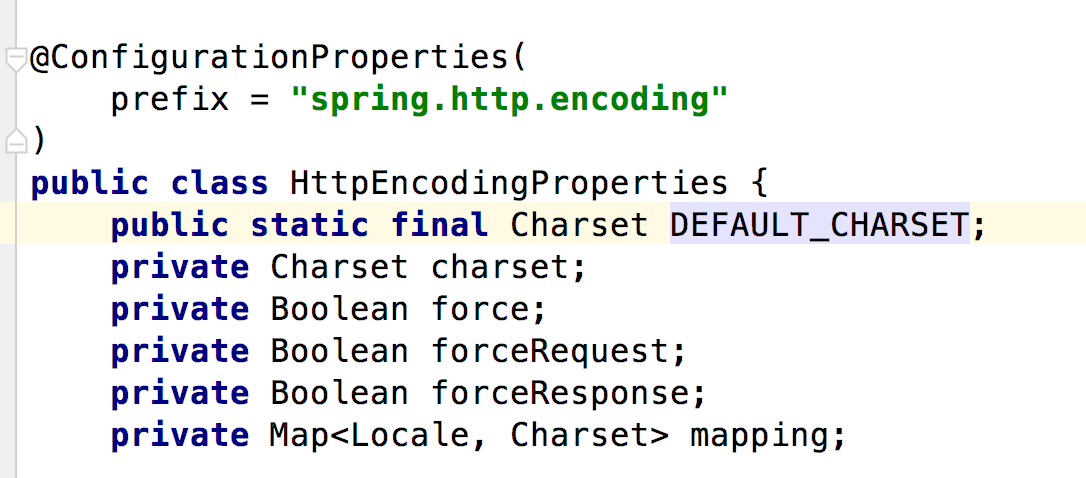
2.4 实例分析:http的编码配置
分析一个简单的springboot内置自动配置功能:http的编码配置
常规:在web.xml中配置filter:
自动配置要满足的条件:
1)能配置CharaterEncodingFilter这个类
2)能配置encoding和farceEncoding两个参数
1. 配置参数
查看源码

代码说明:
1)在application.yml文件中的前缀是 spring.http.encoding
2)默认编码为UTF-8,若要修改,则使用spring.http.encoding.charset=”编码”
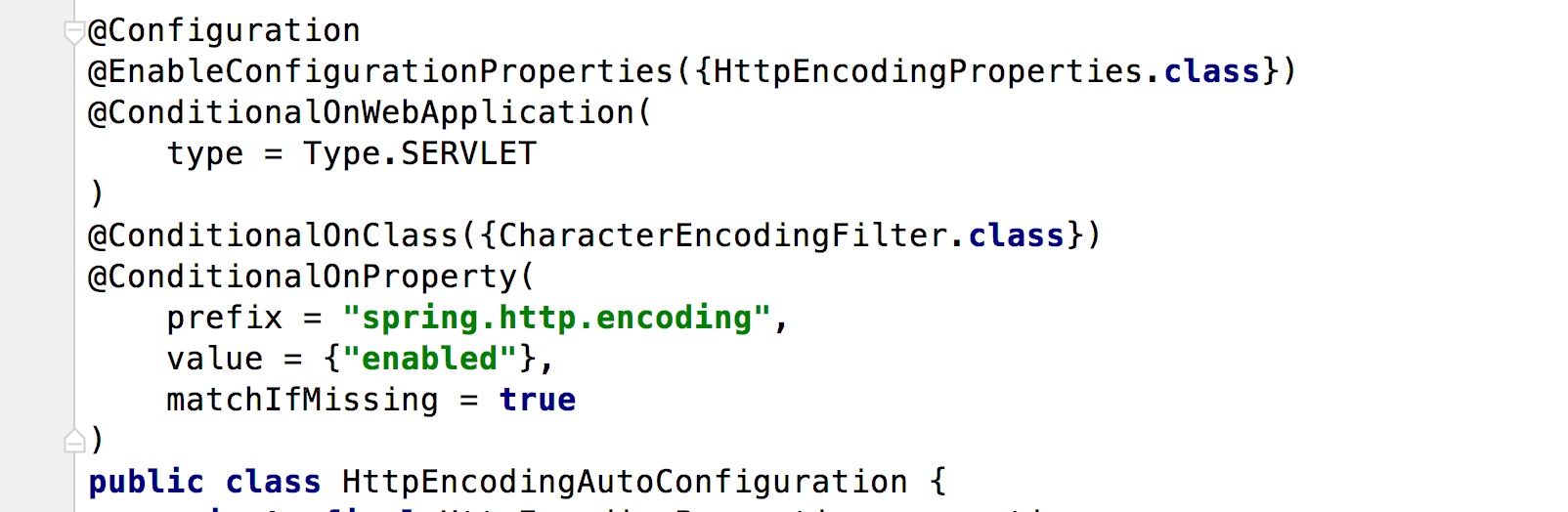
2.配置bean
代码解释:
1)EnableConfigurationProperties属性注入
2)基于条件配置bean: ConditionalOnXXXX
2.5 实战:给自定义类实现自动配置
1 | - 自己写一个自动配置 和 starter pom |
(1)新建maven工程
(2)在pom中添加
1 | <dependency> |
(3)属性配置
1 | import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; |
(4)判断依据类: 根据此类存在与否来,在创建这个类的bean
1 | public class Hello { |
(5)自动配置类:
1 | import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; |
(6)注册配置
1 | org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ |
(7)将以上项目发布到本地仓库,在springboot项目中添加依赖
1 | <dependency> |
(8)使用starter
1 | //等同于同时加上了@Controller和@ResponseBody |
(9)手动配置属性,在yml中添加
1 | hello: |
3 SpringBoot开发干货
3.1 Thymeleaf模版引擎
1 | 1. Spring Boot包括对以下模板引擎的自动配置支持:FreeMarker Groovy Thymeleaf Mustache |
Thymeleaf基础知识
1 | - 是一个java类库,是xml/css/html模版引擎,作为MVC的View |
使用语法教程见【Thymeleaf常用.md】
与SpringMVC集成
SpringBoot的Thymeleaf支持
springboot 通过哦org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf实现自动配置
查看ThymeleafProperties源码,可以看到默认设置的属性,前缀为spring.thymeleaf
部分代码如下:
1 | private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/"; //默认模版放置路径 |
实战
(1)新增starter pom
1 | <dependency> |
(2)pojo
1 | public class User { |
(3)Controller
1 | ("/hello") |
(4)页面 classpath:resources/templates
1 |
|
3.2 SpringBoot整合Mybatis
基本整合
使用mybatis官方提供的mybatis-spring-boot-starter方案
官网文档:http://www.mybatis.org/spring-boot-starter/mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure/index.html
https://github.com/mybatis/spring-boot-starter/wiki/Quick-Start
(1)starter pom : 选mybatis,mysql
1 | <dependency> |
(2)数据源
1 | datasource: |
MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter将:
1 | - 自动检测现有的数据源 |
(3)在启动类添加mapper包扫描
1 | @SpringBootApplication |
这样springboot启动时候会自动扫描包(不建议在每个mapper类中加@Mapper)
(4)Mapper类编写(基于注解,还有原始的基于xml的)
1 | public interface UserMapper { |
pojo
1 | public class User { |
table
1 | CREATE TABLE `USER` ( |
(5)测试
1 | (SpringRunner.class) |
关于事务
1 | springboot自动开启了JDBC事务管理,不需要手动添加 |
逆向工程
使用maven插件方式生成逆向工程
1 | <plugin> |
在以上路径添加generatorConfig.xml
使用 mvn mybatis-generator:generate 或用IEDA即可
分页插件
pagehelper项目地址https://github.com/pagehelper
https://github.com/pagehelper/pagehelper-spring-boot
pom
1 | <!-- 分页插件 --> |
配置
1 | 不需要配置,自动注入配置 |
使用
1 | /* |
3.3 统一异常处理器
3.4 开发热部署
基于IDEA的springboot热部署
1 关闭模版缓存
1 | spring: |
2 pom
1 | <!--热部署--> |
3 IDEA设置
1 | 1. preperences > Build ,Execution,Deplment > compiler > build project automatically |
效果:修改类 > 会重启
3.5 项目部署到linux
springboot部署到linux
jar形式
1 打包:mvn package
2 测试运行:java -jar XXX.jar 即可
3 注册为linux服务
(1)修改spring-boot-maven-plugin
1 | <plugins> |
然后package打包
(2)注册为linux服务
1 | 1. linux安装jdk |