参考:itheima
[TOC]
1 内存四区
1.1 数据类型本质分析
1.1.1 数据类型的本质
Code
1 | #include <stdio.h> |
1.1.2 数据类型的别名
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
1.2 变量的本质分析
Code
1 | #include <stdio.h> |
1.3 程序的内存四区模型
Code
1 | 1)栈区:系统分配空间,系统自动回收,函数内部定义的变量,函数参数,函数结束,其内部变量生命周期结束 |
全局区分析
全局区:全局变量 静态变量 文字常量区
Code
1 |
|
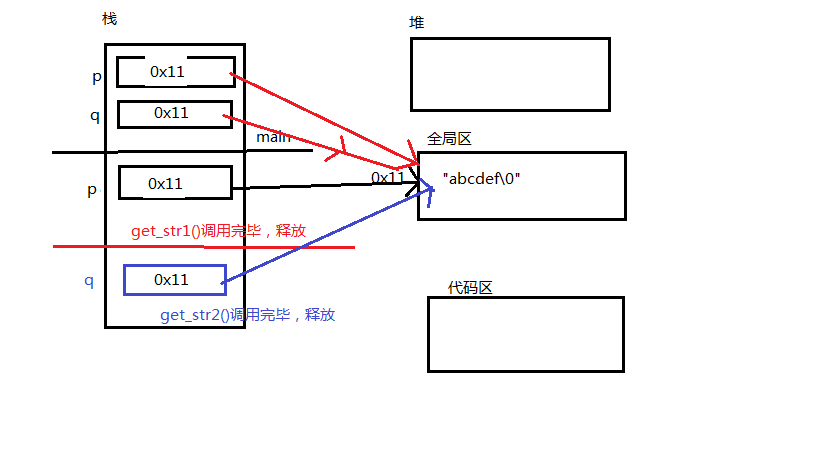
全局区分析
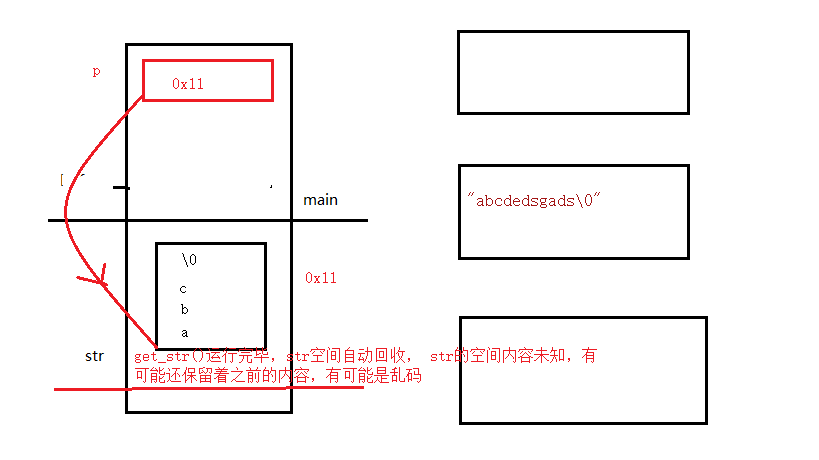
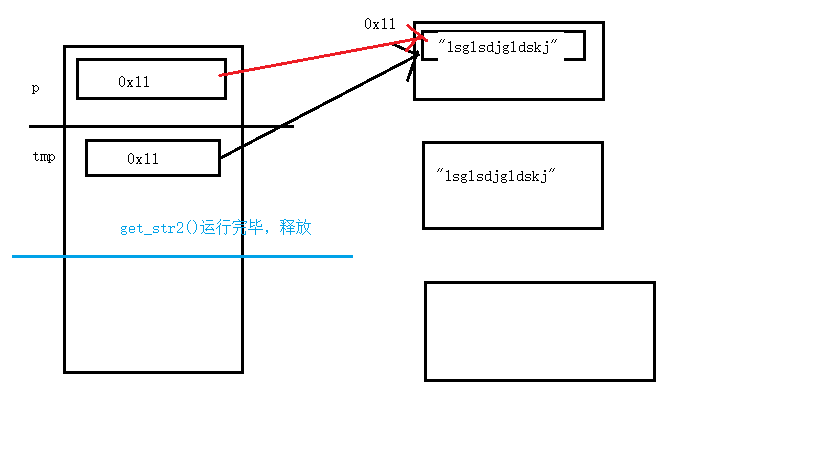
堆栈区分析
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
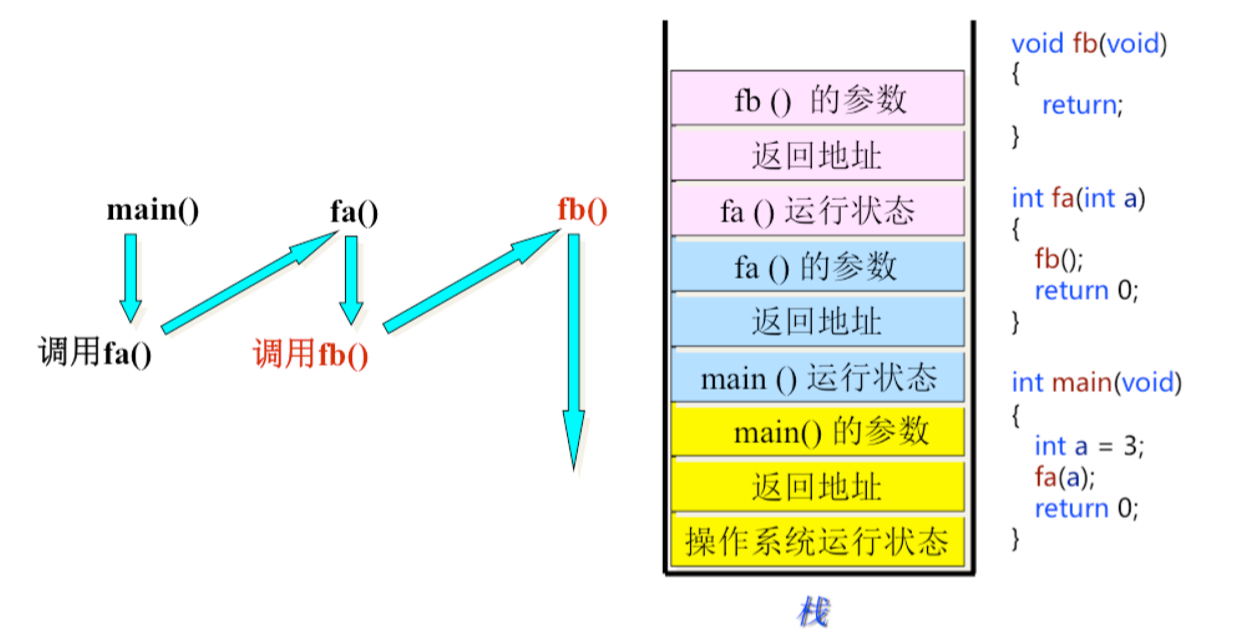
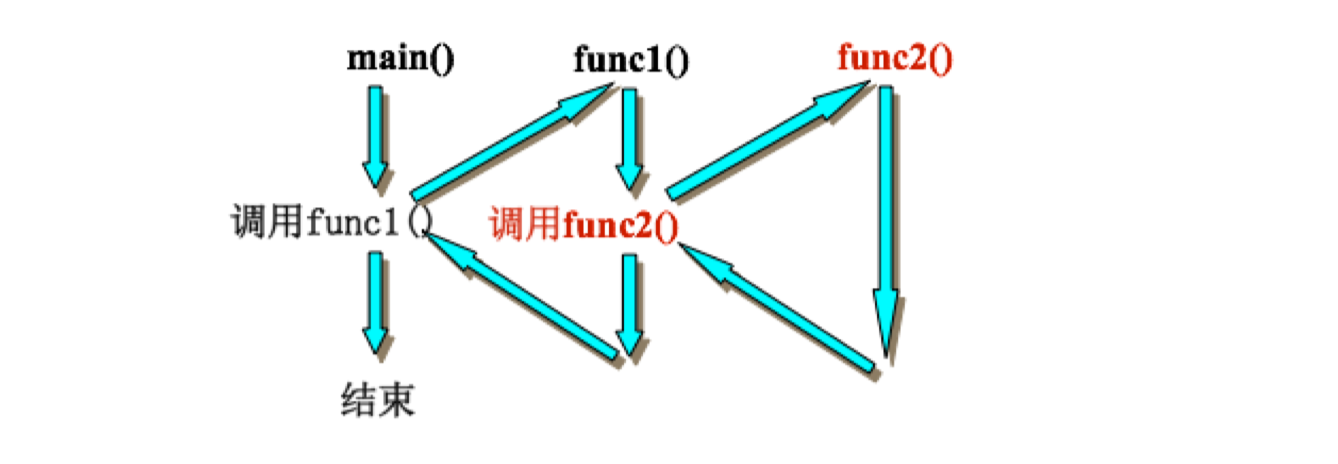
1.4 函数的调用模型
栈:先进后出
1.5 函数调用变量传递分析
Code
1 | 1. main 函数中可以在栈/堆/全局分配内存,都可以被 func1 和 func2 使用 |
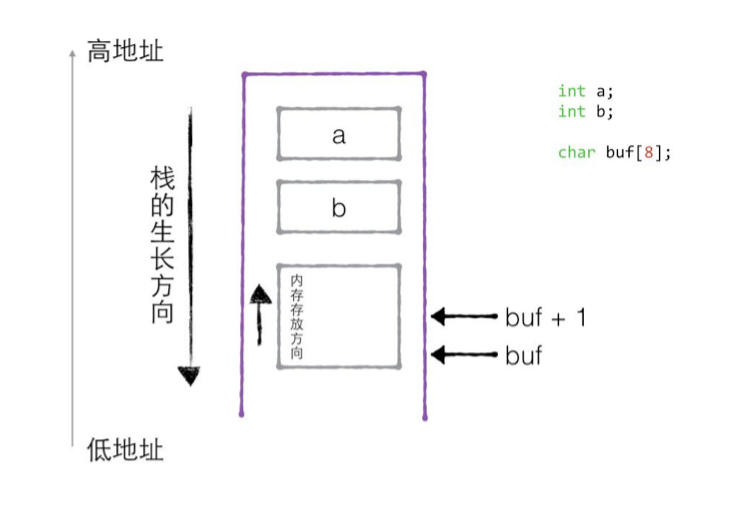
1.6 栈的生长方向和内存存放方向
Code
1 | #include <stdio.h> |
2 指针强化
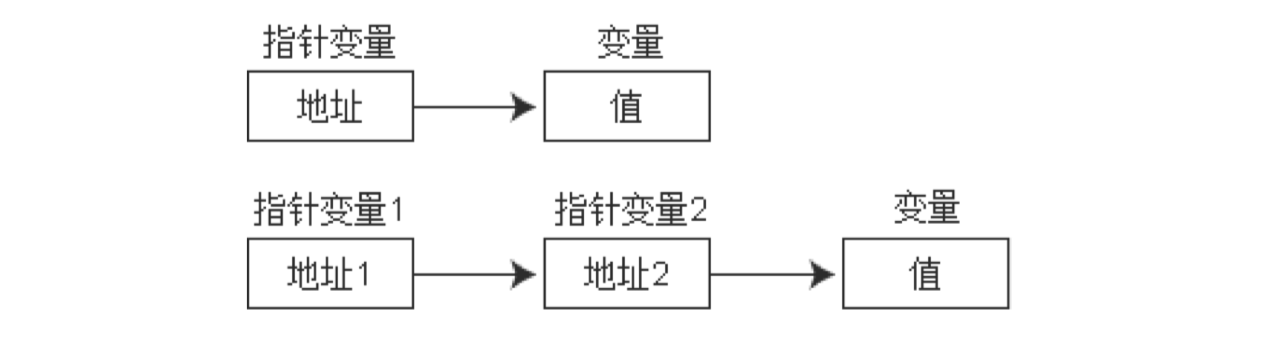
强化 1:指针是一种数据类型
Code
1 | #include <stdio.h> |
指针变量和它指向的内存块是两个不同的概念
Code
1 | #include <stdio.h> |
当我们不断的给指针变量赋值,就是不断的改变指针变量
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
强化 2:间接赋值(*p)是指针存在的最大意义
通过指针间接赋值
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
强化 3:理解指针必须和内存四区概念相结合
指针做参数输入输出特性
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
强化 4:应用指针必须和函数调用相结合(指针做函数参数)
3 字符串
3.1 字符串的基本操作
字符串的初始化
Code
1 | #include <stdio.h> |
字符串拷贝函数的实现
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
3.2 项目开发常用字符串应用模型
strstr中的while和do-while模型
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
两头堵模型
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
3.3 const
const的使用
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
4 二级指针
4.1 二级指针输出特性
二级指针做参数输出特性
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
4.2 二级指针输入特性
二级指针做输入:第一种内存模型
Code
1 | //指针数组 |
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
二级指针做输入:第二种内存模型
c
1 | char myArray[10][30] = {"aaaaaa", "ccccc", "bbbbbbb", "1111111111111"}; |
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
二级指针做输入:第三种内存模型
c
1 | char **myArray = NULL; |
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
5 多维数组
一维数组
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
数组指针
Code
1 | //有typedef:类型 |
Code
1 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS |
多维数组名的本质
c
1 | 1)二维数组初始化 |